Overview of Trochanteric Bursitis
Trochanteric bursitis is a painful condition characterised by inflammation of the bursa, a fluid-filled sac located on the outer aspect of the hip. This bursa acts as a cushion between the bone and tendons, facilitating smooth movement of the hip joint.
Anatomy of the Hip
The hip joint is one of the largest joints in your body. It is a ball-and-socket joint, formed by the head of the femur (thigh bone) and the acetabulum (socket) of the pelvis. In a normal joint the ball part of the joint fits neatly into the socket in your pelvis.
The joint’s bones are covered by a tough but smooth, slippery surface, known as cartilage. This tissue allows the bones to move against each other without friction.
There are also bands of tissue, called ligaments, that connect the ball to the socket, stabilising the hip and forming the joint capsule. The joint capsule is lined with a thin membrane called synovium, which produces a clear fluid that helps to lubricate the joint.
The trochanteric bursa is situated over the greater trochanter, a bony prominence on the outer side of the femur. It lies beneath the iliotibial band (IT band) and covers the hip’s lateral aspect.
Causes of Trochanteric Bursitis
Trochanteric bursitis can be caused by various factors, these can include:
- Repetitive Movements: Overuse or repetitive activities involving the hip, such as running, climbing stairs, or prolonged standing, can irritate the bursa.
- Direct Trauma: A fall or direct impact to the hip can lead to inflammation.
- Muscle Imbalance: Weak hip muscles or an imbalance in muscle strength can alter hip mechanics and contribute to bursitis.
Symptoms of Trochanteric Bursitis
The symptoms of trochanteric bursitis can vary depending on the exact cause and individual patient but will often include some or all of the below:
- Hip Pain: Pain on the outer side of the hip, often worsened by lying on the affected side or walking.
- Tenderness: The area over the greater trochanter may be tender to touch.
- Pain with Movement: Pain during activities that involve hip movement, such as walking, climbing stairs, or getting up from a seated position.
Diagnosis of Trochanteric Bursitis
Diagnosing trochanteric bursitis is quite a straightforward process and your consultant will be able to give you a clear diagnosis at your initial appointment. It will usually involve:
- Physical Examination: Assessment of joining range of movement of the hip and muscle strength of the surrounding muscles. Your consultant will gently palpate the area around the hip to review any pain and tenderness. They will also examine your gait (walking pattern) and evaluate how you move during certain activities.
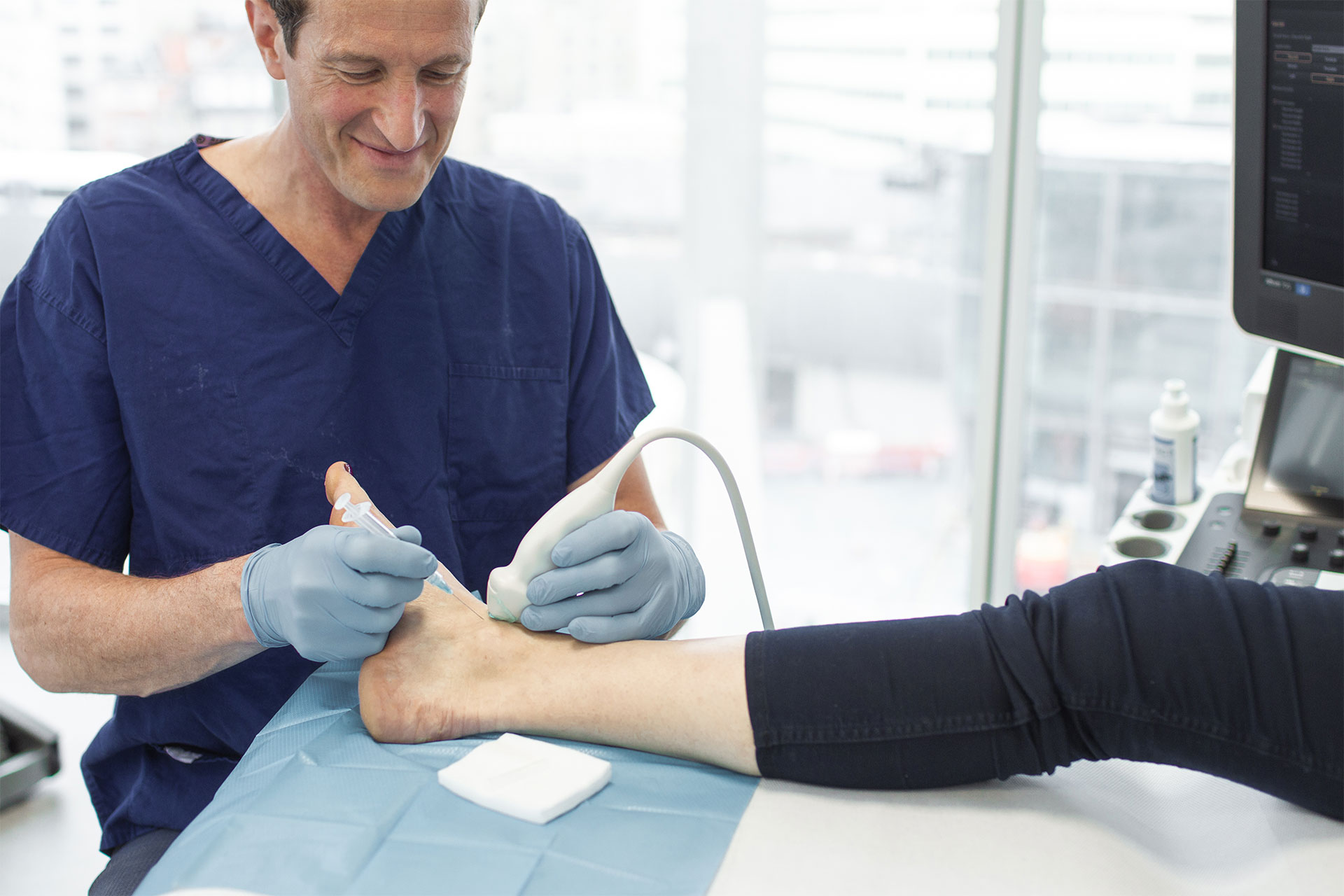
- Imaging: Imaging is not usually necessary, but sometimes X-rays or MRI scans may be ordered to rule out other hip conditions.
Treatment Options
Treatment for trochanteric bursitis aims to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. In nearly all cases it can be managed well with conservative treatment.
Conservative Management for Trochanteric Bursitis
- Rest and Activity Modification: Avoiding activities that aggravate symptoms.
- Anti-Inflammatory Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Physiotherapy: Strengthening hip muscles, improving flexibility, and correcting movement patterns.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections into the bursa can provide temporary relief.
Surgical Options for Trochanteric Bursitis
Surgery is rarely necessary for trochanteric bursitis and is typically considered only after non-surgical treatments have failed to provide relief.
Bursa Removal: In cases of severe and persistent bursitis, surgical removal of the inflamed bursa may be considered.
Questions and Answers
Can trochanteric bursitis recur after treatment?
Yes, trochanteric bursitis can recur, especially if underlying causes like muscle imbalances or overuse are not addressed. Physiotherapy is a vital part of your recovery.
Is rest important for treating trochanteric bursitis?
Yes, rest and activity modification are often recommended to allow the inflamed bursa to heal.
How long does it take to recover from trochanteric bursitis?
Recovery time varies depending on the severity of the condition and the effectiveness of the chosen treatment plan. It may take several weeks to a few months for symptoms to fully resolve.
Can trochanteric bursitis lead to other hip problems?
While trochanteric bursitis itself is a localised condition, untreated imbalances or movement issues can potentially contribute to other hip problems over time.
Is surgery the first-line treatment for trochanteric bursitis?
No, surgery is generally considered when conservative treatments have failed to provide relief. Most cases of trochanteric bursitis can be successfully managed with non-surgical approaches.