Olecranon bursitis is a common condition that affects the back of the elbow, causing noticeable swelling, pain, and sometimes redness. It occurs when the small fluid-filled sac (bursa) that sits between the skin and the point of the elbow (olecranon) becomes inflamed. The condition may arise suddenly from trauma or develop gradually from repetitive pressure or infection. While often mild and self-limiting, in some cases olecranon bursitis may require medical treatment to reduce inflammation, drain fluid, or treat infection.
Anatomy of the Elbow Bursa
The olecranon bursa is a thin sac of fluid that lies between the skin and the olecranon—the bony prominence at the tip of the elbow. Its function is to reduce friction and cushion the movement of the skin over the underlying bone when the elbow bends and extends. When irritated or inflamed, the bursa fills with excess fluid, resulting in a soft, sometimes painful swelling.
Causes of Olecranon bursitis
Olecranon bursitis can result from a single traumatic event, prolonged pressure, or underlying systemic conditions.
Mechanisms and contributing factors include:
Acute trauma: A direct blow to the tip of the elbow (e.g. falling onto a hard surface or knocking the elbow) can cause immediate bleeding into the bursa or trigger inflammation, leading to rapid swelling.
Chronic repetitive pressure: Frequently leaning on the elbow (known as “student’s elbow”) irritates the bursal lining over time. This is commonly seen in:
- Office workers and students
- Plumbers, mechanics, and tradespeople
- Wrestlers, martial artists, or rugby players who fall repeatedly on the elbow
Infection (septic bursitis): A small wound, insect bite, or abrasion near the elbow can allow bacteria to enter the bursa, leading to pus formation, warmth, redness, and systemic symptoms.
Crystal arthropathies: Gout or pseudogout can cause crystal deposition within the bursa, triggering inflammation even without infection.
Rheumatoid arthritis or autoimmune disease: Inflammatory conditions may predispose the bursa to chronic irritation and swelling.
Poor elbow biomechanics or overuse: Excessive repetitive elbow flexion/extension in sports like:
- Throwing sports (cricket, baseball, javelin)
- Weightlifting
- Push-up heavy fitness programmes
These can all provoke irritation of the olecranon bursa.
Symptoms of Olecranon bursitis
Presentation can vary depending on whether the bursitis is acute or chronic, and whether infection is involved.
Key features include:
- Swelling over the back of the elbow: This is typically the first and most obvious sign. The swelling may appear gradually over days or suddenly after trauma. It often feels soft and fluctuant, like a small water balloon.
Pain or tenderness:
- Pain may be mild in non-infective bursitis.
- In traumatic cases, patients may report bruising and soreness.
- Infected bursitis is significantly more painful and may cause throbbing or a burning sensation.
- Redness and warmth: If the overlying skin is red or hot to touch, this may suggest infection or acute inflammation.
- Limited elbow extension: Large swellings can physically restrict full movement, and discomfort may discourage patients from fully straightening the arm.
- Signs of systemic illness: In cases of septic bursitis, fever, chills, and malaise may develop. The area may also become more tense and firm if pus is collecting.
- Recurrent episodes: Patients who repeatedly rest on their elbow or have underlying gout may notice frequent flare-ups or chronic swelling.
Diagnosis of Olecranon bursitis
Diagnosis is primarily clinical, based on physical examination and patient history. Further investigations may be needed to rule out infection or underlying causes:
- Clinical examination: A soft, fluctuant swelling over the tip of the elbow is characteristic.
- Aspiration: In suspected septic bursitis, a small amount of fluid may be drawn from the bursa to test for infection or crystals.
- Blood tests: May be used to detect signs of infection, gout, or inflammatory conditions.
- Imaging: Ultrasound: Can confirm fluid collection and guide aspiration or injection. X-rays: May be performed to exclude bony injuries or gouty tophi.
Differential Diagnosis
Other conditions that can mimic olecranon bursitis include:
- Gout or pseudogout (without bursal involvement)
- Soft tissue masses or lipomas
- Elbow cellulitis
- Rheumatoid nodules
- Triceps tendon injury or enthesopathy
- Elbow fracture (in trauma cases)
Treatment Options for Olecranon bursitis
Non-Surgical Management
Most cases of olecranon bursitis resolve with simple measures:
- Rest and avoidance of pressure on the elbow
- Ice application: Helps reduce swelling and discomfort in the acute phase
- Compression bandages or elbow pads: To reduce swelling and prevent further irritation
- NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs): Such as ibuprofen or naproxen for pain and inflammation
- Aspiration: In cases of significant swelling or pain, fluid may be drained with a needle under sterile conditions. This also helps confirm diagnosis if infection or gout is suspected.
- Antibiotics: Required if the bursa is infected (septic bursitis). Oral antibiotics are usually effective; IV antibiotics may be necessary in more severe cases.
Most patients improve within a week or two of appropriate treatment.
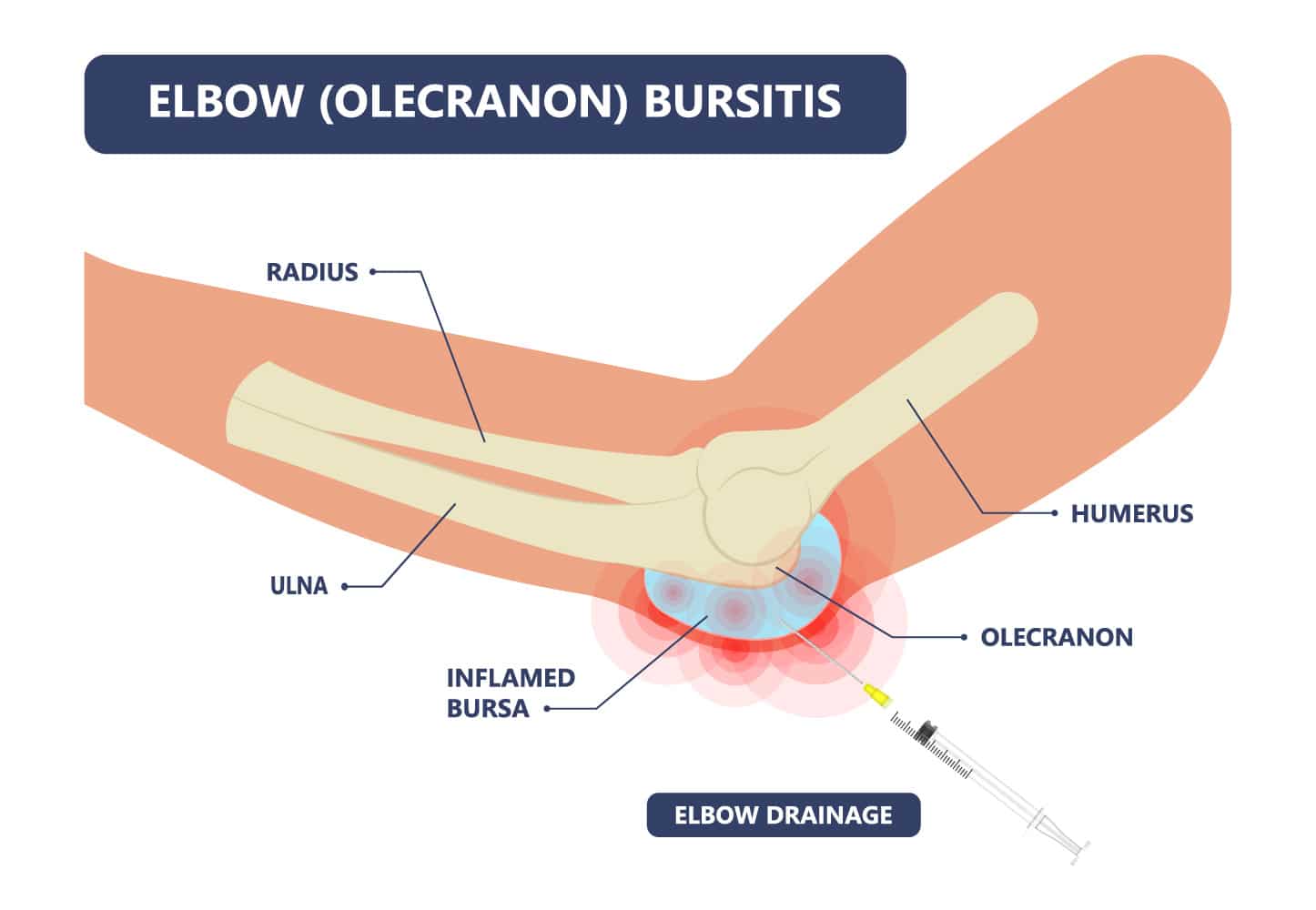
Surgical Options
Surgery is rarely required but may be indicated in:
- Chronic or recurrent bursitis not responding to conservative treatment
- Infected bursae that do not improve with aspiration and antibiotics
- Significant calcification or thickening of the bursa causing persistent symptoms
Procedure:
- Bursectomy: Surgical removal of the bursa can be performed under local or general anaesthesia. It’s typically a day-case procedure.
Recovery:
- Most patients return to light activity within 1–2 weeks.
- Full recovery with minimal scarring and restored function is expected.
- Wearing a protective pad post-operatively can reduce recurrence risk.
Frequently Asked Questions
Will olecranon bursitis go away on its own?
Yes, in many cases it resolves with rest, ice, and avoiding pressure on the elbow. However, infected bursitis needs medical treatment.
How can I tell if my bursitis is infected?
Signs of infection include redness, warmth, fever, and significant tenderness. If you suspect infection, seek urgent medical advice.
Can I still exercise with olecranon bursitis?
Low-impact activities are usually safe, but avoid weight-bearing on the elbow or any movements that aggravate the swelling.
How is it different from elbow arthritis or tendonitis?
Bursitis affects the bursa (fluid sac), whereas arthritis affects the joint and tendonitis involves the tendons. A clinician can distinguish between them during assessment.
Can it come back?
Yes, especially if repetitive pressure on the elbow continues. Wearing protective pads, improving ergonomics, and addressing underlying conditions (like gout) can help prevent recurrence.