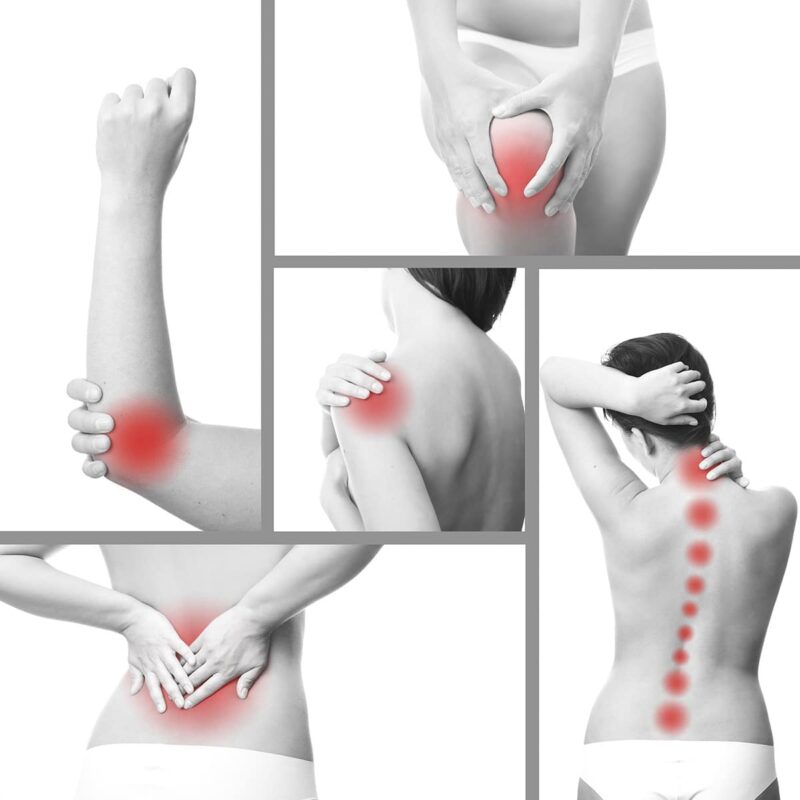
Menopause is a natural phase in a woman’s life and marks the end of her reproductive years. In this blog, we will explore how menopause influences joint pain and bone health, the role of hormones, causes of pain, and available treatment options.
Overview: Understanding Menopause
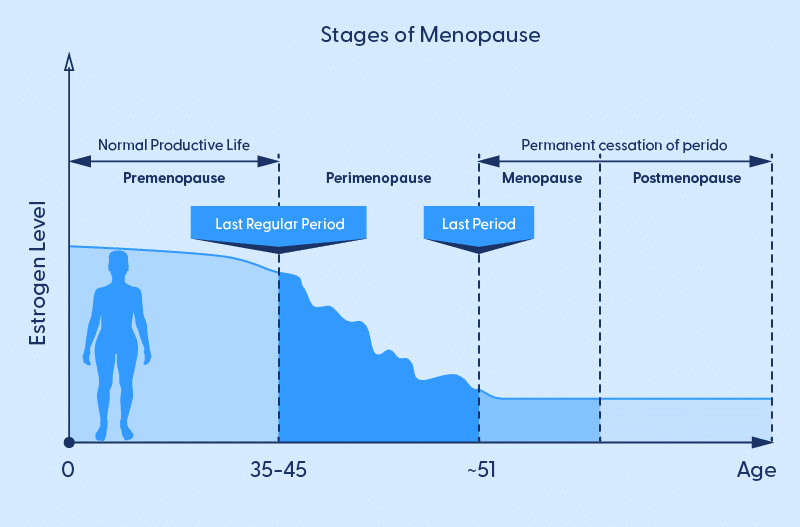
Perimenopause and menopause typically occur in a woman’s mid to late 40s or early 50s, although it can happen earlier or later. Menopause occurs due to a natural decline in hormones, primarily estrogen and progesterone and is defined as the cessation of menstruation for at least 12 consecutive months. Leading up to this, women go through a transitional period which brings about significant hormonal changes and a range of various symptoms; one often overlooked aspect of menopause is its impact on joint health and bone density.
The Role of Hormones: Estrogen and Bone Health
Estrogen, a key female sex hormone, plays a significant role in maintaining bone health. It helps regulate osteoclasts’ activity (cells that break down bone) and osteoblasts (cells that build bone).
During menopause, estrogen levels decline, leading to several effects on bone health
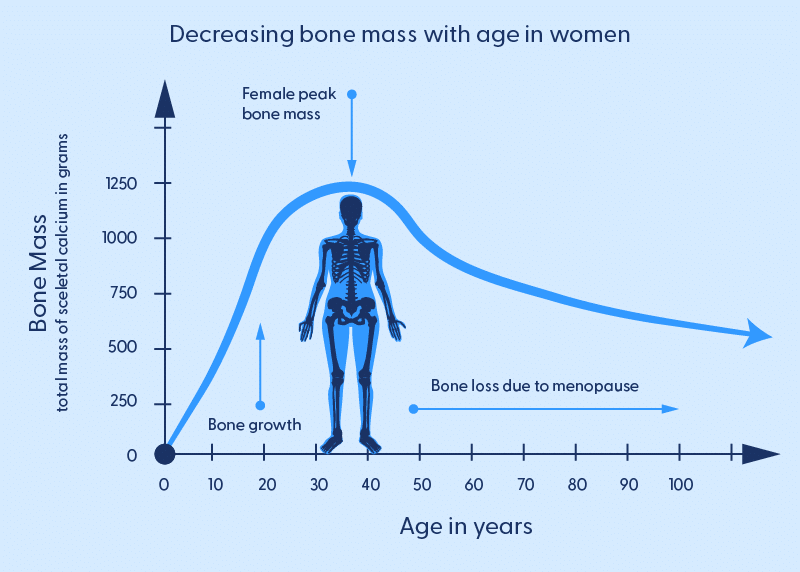
Increased Bone Resorption:
Estrogen’s decline results in a higher rate of bone resorption (breakdown) by osteoclasts, which can lead to bone loss and reduced bone density.
Reduced Bone Formation:
Lower estrogen levels also affect osteoblasts, leading to decreased bone formation.
Increased Bone Fracture Risk:
Weakened bones due to reduced bone density are more susceptible to fractures, especially in weight-bearing joints like the hips and knees.
Causes of Joint Pain During Menopause:
Osteoarthritis:
Menopause can contribute to the development or worsening of osteoarthritis, a common joint condition. With estrogen’s decline, less joint protection and lubrication leads to increased wear and tear.
Hormonal Fluctuations:
Hormonal fluctuations during perimenopause (the transition phase before menopause) can lead to changes in joint tissue, making them more susceptible to inflammation and pain.
Muscle Weakness:
Reduced estrogen levels can lead to muscle weakness, reducing joint support and stability.
Weight Gain:
Many women experience weight gain during menopause, which places additional stress on the joints, especially the knees and hips.
Treatment Options:
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT):
HRT involves using estrogen or a combination of estrogen and progesterone to alleviate menopausal symptoms and potentially protect bone health. However, the use of HRT is subject to individual health considerations and should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
Physical Activity:
Regular exercise can help maintain joint flexibility, strengthen supporting muscles, and improve overall bone health. Weight-bearing exercises, such as walking and weightlifting, can be particularly beneficial.
Dietary Choices:
A diet rich in calcium and vitamin D is essential for maintaining bone health. Calcium is crucial for bone density, and vitamin D aids in its absorption. Dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods are good sources.
Medications:
Medications like bisphosphonates may be prescribed to prevent further bone loss or improve bone density. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help manage joint pain and inflammation.
Physiotherapy:
Physical therapists can provide tailored exercises and strategies to alleviate joint pain, improve flexibility, and strengthen muscles.
Questions and Answers:
Q1: Does menopause cause joint pain in all women?
A1: Not all women experience joint pain during menopause, but it is more common due to hormonal changes and other contributing factors.
Q2: Can HRT prevent joint pain and bone loss during menopause?
A2: HRT can help alleviate some symptoms and potentially protect bone health. However, its use should be carefully considered in consultation with a healthcare provider.
Q3: Are there dietary supplements to improve bone health during menopause?
A3: Calcium and vitamin D supplements can be beneficial, but it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider for proper dosages and guidance.
Q4: What type of exercise is best for joint health during menopause?
A4: Weight-bearing exercises, such as walking, jogging, and weightlifting, can help maintain joint health. It’s also very important to build muscle strength to support your joints. You might also find lower-impact activities like swimming and cycling are also beneficial if you are experiencing joint pain.
Q5: How can I differentiate between menopausal joint pain and other joint conditions?
A5: If you’re experiencing joint pain during menopause, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and to rule out other joint conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis.